Carbon nanotubes for polarised light detection
Using carpets of aligned carbon nanotubes, researchers from Rice University and Sandia National Laboratories have created a solid-state electronic device that is hardwired to detect polarised light across a broad swathe of the visible and infrared spectrum.
“Many animals and insects can see polarised light and use it for navigation, communication and more. Humans can’t see polarised light, so we rely on devices to do that for us,” said Rice’s Junichiro Kono, professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics and astronomy. Most devices can’t detect polarised light directly. Instead, engineers place a grate or filter in front of the detector.
“Our photodetector discerns polarised light intrinsically, much like the photoreceptors in the eyes of animals and insects that see polarised light,” said François Léonard at Sandia National Laboratories, one of the lead researchers on the study.
Polarised light consists of individual electromagnetic waves oscillating parallel to one another. The effect is created when light reflects from a transparent material, which is why polarised sunglasses reduce the glare from water, glass and other surfaces. Astronomers use polarised light in a number of ways, and there are a number of applications for polarimetry in communications and the military.
Credit: X He/Rice University
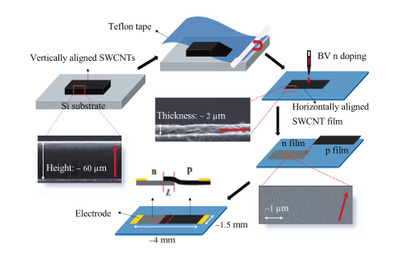
The nanotube carpets used in the photodetectors are grown in the lab of Rice chemist Robert Hauge. Each nanotube carpet contains dozens of varieties of nanotubes, and about two-thirds of the varieties are semiconductors. Because each of the semiconducting varieties interacts with a specific wavelength of light, Kono’s team was able to show in its earlier work that the flattened, aligned carpets of nanotubes could serve as broad-spectrum photodetectors.
In the ACS Nano study, lead author Xiaowei He, a graduate student in Kono’s group, used chemicals called ‘dopants’ to alter the electrical properties of the nanotube carpets. He created two types of carpet, one with positively charged carriers (p-type) and another with negatively charged carriers (n-type). By overlapping sections of these two, He and colleagues created a device called a p-n junction, which is a fundamental building block of microelectronics.
“Our work provides a new path for the realisation of polarisation-sensitive photodetectors that could be enabled on flexible or non-planar surfaces,” He said. Study co-authors include Hauge, Xuan Wang, Kankan Cong and Qijia Jiang, all of Rice; Léonard, Alexander Kane and John Goldsmith, all of Sandia; and Sébastien Nanot, formerly of Rice and now with the Institute of Photonic Sciences in Barcelona, Spain.
Next-gen semiconductor material for light-based electronics
Scientists from the University of Edinburgh have created a new type of material that could enable...
Chip-scale optical amplifier enhances data and sensing
Energy-efficient and small enough to fit in a smartphone, an optical amplifier developed at...
Organic transistor 'limitation' improves stability
Researchers have shown that a longstanding organic transistor design limitation actually improves...




